Health Hazards: Avoid Using Newspapers for Food Packaging and Serving
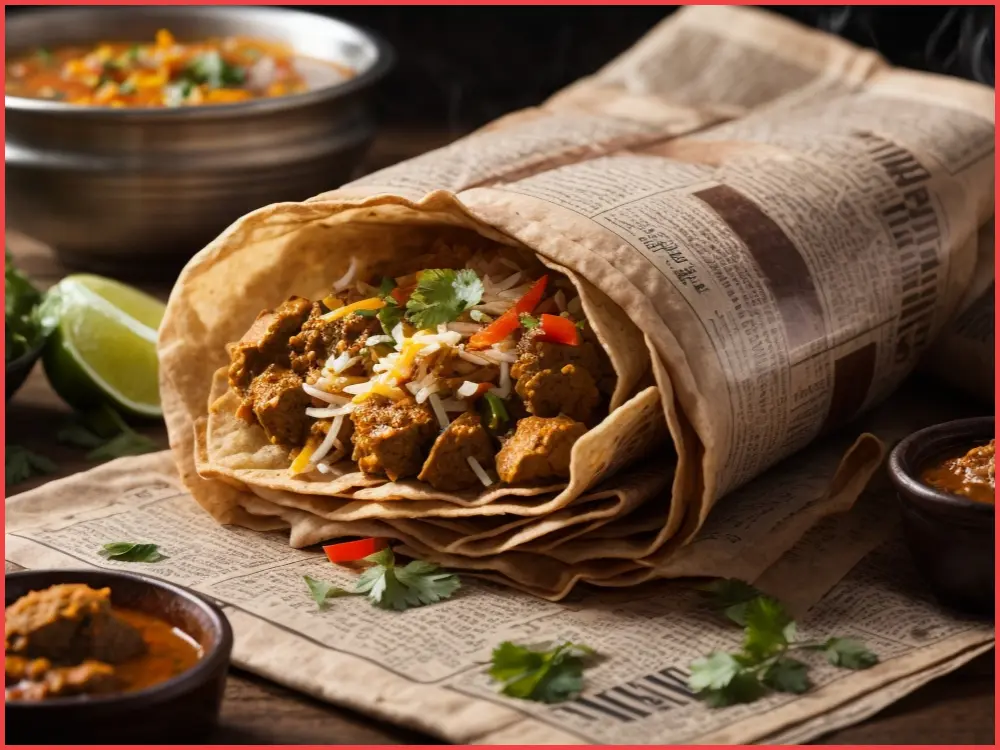

In a significant move aimed at safeguarding public health, the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has issued a stern advisory, urging both consumers and food vendors to immediately cease the use of newspapers for packing, storing, and serving food items. This proactive step by FSSAI highlights the alarming health risks associated with the practice of utilizing newspapers for these purposes. The ink used in newspapers, the FSSAI warns, contains certain chemicals that can have detrimental effects on human health. This article delves into the rationale behind FSSAI’s advisory and explores the potential health hazards linked to newspaper use in food handling.
Why You Should Avoid Wrapping Food In Newspaper? What Are The Health Risks Involved?
G Kamala Vardhana Rao, the CEO of FSSAI, has shed light on the hazards associated with employing newspapers for wrapping and packaging food items. According to the regulatory body, the ink used in newspapers contains “various bioactive materials” that can prove harmful to health. Mr. Rao explicitly states, “The ink used in newspapers contains various bioactive materials with known negative health effects, which can contaminate food and lead to health issues when ingested.”
The concerns extend beyond ink composition. Newspapers, during their lifecycle, are often subjected to diverse environmental conditions, making them susceptible to contamination by bacteria, viruses, or other pathogens. When such contaminated newspapers come into contact with food, they can potentially transfer these harmful microorganisms, thus posing a significant risk of foodborne illnesses. Therefore, using newspapers as a medium for food storage or serving is inherently unsafe and should be avoided at all costs.
Regulatory Measures to Curb Newspaper Use in Food Handling
To reinforce the importance of food safety, the FSSAI has introduced the Food Safety and Standards (Packaging) Regulations, 2018. This regulatory framework expressly prohibits the use of newspapers or similar materials for storing, packing, or wrapping food items. Both consumers and food vendors are now mandated to abstain from using newspapers for covering or serving edible items. Moreover, newspapers should not be utilized to absorb excess oil from fried foods, such as samosas or pakodas.
In light of this regulatory framework, it is incumbent upon all stakeholders in the food industry to adhere to these guidelines. FSSAI is actively collaborating with state food authorities to ensure strict compliance with these regulations, with the aim of completely eradicating the use of newspapers in food handling.
Promoting Safer Alternatives for Food Packaging and Serving
G Kamala Vardhana Rao, in issuing this cautionary advice, has emphasized that FSSAI is dedicated to ensuring the safety of the food supply across the country. By discouraging the use of newspapers and promoting the adoption of safer alternatives for food packaging and serving, FSSAI is reaffirming its commitment to safeguarding public health.
Consumers and food vendors must recognize the critical importance of proper food storage and handling. The potential health risks associated with using newspapers as a means to wrap, pack, or serve food are simply too significant to ignore. To mitigate these risks and ensure the well-being of all, it is imperative to consider safer alternatives that adhere to FSSAI’s guidelines.
Exploring Safer Food Packaging and Serving Options
Given the hazards associated with newspaper use, it becomes essential to explore safer alternatives for food packaging and serving. Fortunately, there are numerous options available that not only eliminate health risks but also contribute to better food hygiene. Here are some alternatives that individuals and food businesses can consider:
Food-Grade Packaging Materials: Opt for food-grade packaging materials such as plastic containers, glass jars, and aluminum foil. These materials are specifically designed for food storage and are less likely to transfer harmful substances to the food.
Biodegradable Packaging: Biodegradable and compostable packaging options are gaining popularity as eco-friendly alternatives. These materials are safe for food contact and have minimal impact on the environment.
Stainless Steel Containers: Stainless steel containers are durable and can be used repeatedly for food storage. They are easy to clean and do not pose any health risks.
Silicone Food Wraps: Silicone food wraps are reusable and provide an airtight seal for food items. They are a sustainable choice for covering bowls and plates.
Paper-Based Food Wraps: If you prefer a paper-like texture for wrapping sandwiches or snacks, consider using parchment paper or wax paper. These options are designed for food use and do not contain harmful inks or chemicals.
Cloth Food Covers: Cloth food covers, often made from cotton or linen, can be used to cover dishes and bread. They are washable and can be a stylish addition to your kitchen.
BPA-Free Plastic Wrap: When using plastic wrap, ensure it is labeled as BPA-free to reduce exposure to potentially harmful chemicals.
By adopting these alternatives, individuals and businesses can prioritize food safety while also contributing to a healthier and more sustainable food ecosystem.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the advisory issued by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) serves as a vital reminder of the importance of safe food handling and packaging practices. The risks associated with using newspapers for food storage, packing, or serving are significant and extend beyond ink composition to potential contamination from environmental factors. To safeguard public health, it is crucial for consumers and food vendors to adhere to FSSAI’s guidelines and embrace safer alternatives for food packaging and serving. By making informed choices and prioritizing food safety, we can collectively ensure the well-being of individuals and communities across India.